VMI’s latest Sustainability Report offers a detailed insight into how the company is integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles into its operations.
A Company-Wide Commitment
VMI has published its Global Sustainability Report 2024, outlining a clear belief that sustainability is not an optional extra, but a fundamental driver of innovation, resilience and competitiveness in a rapidly changing global marketplace.
The report makes clear that sustainability is a responsibility shared across the business. It is not confined to a single department, but integrated into the company’s corporate strategy and overseen by dedicated governance structures. VMI aligns its reporting with international frameworks, ensuring that progress is measured consistently, can be tracked year-on-year, and is communicated transparently, subject to external scrutiny. This is an exceptional thing to do for any organisation working with raw materials, and it is a standard that the industry should look to adopt more.
This approach, from VMI, positions sustainability as a business-wide commitment, where employees at all levels are expected to contribute to long-term objectives. By embedding it in strategic planning and day-to-day operations, VMI seeks to ensure that improvements are continuous, rather than reactive.
Tackling Environmental Impact
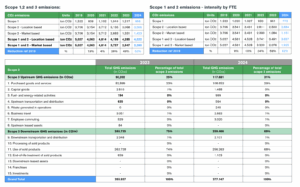
Environmental performance is the most data-driven element of the report. The company has set a clear target of achieving carbon-neutral operations by 2030, and progress is already visible. Renewable energy now accounts for a growing share of electricity consumption, while electrification continues to expand across the vehicle fleet and logistics operations.
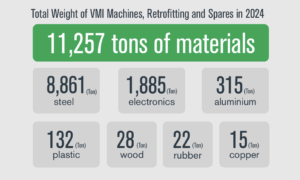
A strong emphasis is placed on the principles of a circular economy. VMI’s machines are increasingly designed with longevity and modularity in mind, allowing customers to extend machine lifespans through upgrades, retrofits and maintenance services. At the same time, recyclability at the end of life is a design priority, helping to close material loops.
Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) now cover more than two-thirds of machine production, identifying practical opportunities to reduce environmental impact across the full product lifecycle. By focusing not only on its own emissions but also on the efficiency of the machinery it supplies, VMI extends the reach of its sustainability efforts into customer operations worldwide.
Waste management remains another area of progress. The company has reduced the use of hazardous substances, improved recycling rates and minimised landfill disposal. These changes demonstrate how environmental responsibility is being integrated into both production processes and product design.
People at the Centre

Alongside environmental performance, the report highlights social responsibility as a central pillar. Workplace safety continues to improve, supported by proactive health and safety programmes, and the company has expanded training and upskilling initiatives to prepare employees for the demands of digitalisation and sustainable manufacturing.
Employee satisfaction scores remain strong, but VMI acknowledges that more can be done in areas such as diversity, equity and inclusion. Rather than presenting this as a completed achievement, the company has committed itself to further progress, recognising that inclusive workplaces are vital to long-term success.
Beyond its internal workforce, VMI invests in education and community engagement. Vocational training and partnerships with local institutions support skill development in the regions where the company operates. Supplier development is also a key focus, with sustainability performance becoming an increasingly important condition for long-term partnerships. This approach creates a ripple effect across the value chain, ensuring that sustainability standards extend well beyond VMI’s direct control.
Governance with Integrity
Governance is described as the backbone of VMI’s sustainability strategy. The company has strengthened its compliance framework, reinforced its Code of Conduct and created clear oversight structures that link directly into corporate decision-making.
Transparency is given particular emphasis. By aligning its reporting with international standards and subjecting its progress to external verification, VMI seeks to demonstrate that its commitments are not aspirational statements but measurable objectives. Independent assessments have already recognised this progress, with the company moving up in global sustainability rankings in 2024.
Driving Innovation
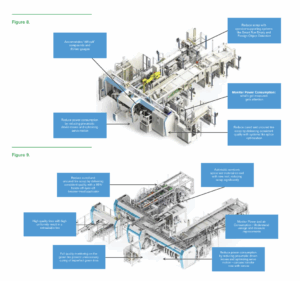
Innovation emerges as one of the strongest themes of the report. The company presents sustainability not as a constraint, but as a catalyst for engineering progress. Machines such as the UNIXX Belt Maker and the REVOLUTE system have been developed to reduce energy use, material waste and production scrap, directly aligning customer efficiency gains with environmental benefits.
Digital technologies also play a prominent role. Predictive maintenance and advanced monitoring systems are now integral to new machinery, helping customers reduce downtime, minimise waste, and extend the service life of their equipment. These tools demonstrate how innovation can simultaneously advance customer competitiveness and sustainability performance.
The report also underlines how sustainability priorities are shaping research and development investments. With more than 5% of its annual turnover invested in R&D, VMI is directing resources into new technologies that combine efficiency, productivity, and environmental responsibility.
Looking Ahead
VMI has established a number of forward-looking goals that strike a balance between ambition and accountability. These include achieving absolute reductions in carbon emissions, further increasing recycling rates, broadening supplier sustainability programmes and continuing to expand investment in education and workforce development.
These targets are not presented as optional enhancements, but as central to long-term resilience and growth of the business. By aligning them with both global standards and customer expectations, VMI positions sustainability as a foundation for its business strategy.
The Bigger Picture
What emerges from the report is a picture of a company that is both realistic about the scale of the challenges it faces and confident in its ability to respond to them. The combination of measurable environmental data, employee-focused initiatives and customer-centred innovation highlights a balanced approach that seeks to combine responsibility with competitiveness. It gives us a sense of openness about the company’s efforts that is essential to the future of our industry. VMI is taking the bull by the horns and making transparency a key facet of their operation, which is commendable. In an industry where greenwashing remains a concern, VMI is making an effort to provide evidence of genuine progress, supported by clear metrics and independent validation. The underlying message is straightforward: sustainability is not a burden, but a pathway to innovation, trust and long-term value creation. Harm Voortman, President & CEO, wrapped up the report, noting: “I am filled with optimism and excitement for the future. Together, we will continue to innovate, grow, and contribute to a more sustainable future.”